Diseases of respiratory system are quite common during any pediatric oe group. These diseases include common cold, upper respiratory tract infection, primary complex, pronchiolitis, bronchial asthma, pneumonia, bronchopneumonia and forelgn body in respiratory tract leading to various complications. In children most of the time otitis media is due to complication of upper respiratory tract infection.
Diseases like upper respiratory tract infection, otitis media, and bronchial asthma occur repeatedly & parents are quite concerned about the repetitive nature of these diseases. In such cases treatment of acute attack is important, but along with that some attempt should be made to prevent the further attacks.

Diseases of Respiratory System
Diseases of Respiratory System in Kids
Disease like primary complex is difficult to diagnose because there is no single parameter which can prove or disprove the diagnosis. A logical approach is required to correlate various findings to confirm the diagnosis of primary complex.
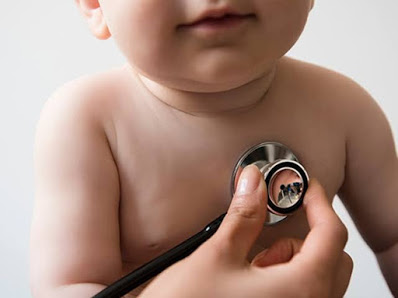
Detecting respiratory signs in small or uncooperative child is a skilled job. Movements of alae nasi, sub costal and Intercostal retraction and wheezing, naving problem of respiratory system these finding reveal that child is and careful auscultation of chest is required in such cases. Auscultatory findings of respiratory system are better appreciated on the posterior side (back). Auscultate the back carefully when the child is in mother’s arm.
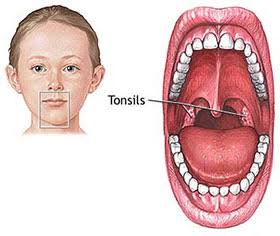
Enlarged cervical lymph node partic- ularly near the angle of the mandible indicate the diseases of pharynx, tonsils and oral cavity, careful throat examination is required in such cases.
Common Cold-Most common Diseases of respiratory system
Running of the nose is the common complaint during any pediatric age group. In majority of cases it is due to viral infection (common cold) like influenza, para influenza.
Predisposing Factors for common cold
Sudden change in climate, overcrowd- ing, increased susceptibility during the epidemic of viral infection like influenza.
Symptoms of commmon cold
The child may present with-
1. Running of nose: Watery discharge from nose along with sneezing
2. Fever and irritability: Due to viremia
3. Excessive crying: Due to blockage of opening of eustachian tube and pressure over ear drums
4. Irritation of throat: Due to post nasal drip
5. Watering of eyes
6. In complicated cases there might be purulent discharge from nose or ear (due to secondary infection)
Signs of common cold
1. Irritable child with mild to moderate fever
2. Watery discharge from nose and eyes
3. Congestion of nasal mucosa, there might be conjunctival congestion- mainly at lateral angle of the eyes
4. In complicated cases there might be tenderness over para nasal sinuses, congestion of throat and discharge from ear
5. No respiratory auscultatory signs
Differential Diagnosis Running of Nose
1. Allergic Rhinitis
a. History of repeated attacks
b. Associated symptoms and signs such as wheezing, bron- chospasm
2. Bacterial Infection of Upper Respiratory Tract
a. Moderate to high fever
b. Purulent discharge from nose
C. Congestion of throat or tonsils might be present
d. Palpable cervical lymph nodes near the angle of the mandible
3. Foreign Body in the Nose
a. Unilateral discharge from nose
b. May be associated with bleeding from nose
4. Nasal Polyp
a. Difficulty in breathing from affected nostril b. Discharge from the same nostril
5. Syphilitic Snuffles
Though rare, other signs of con- genital syphilis should be looked for if the running of nose is associated with ulceration of nasal mucosa, excoriation of upper lip and de- pressed nasal bridge.
Investigations of Diseases of Respiratory System
In uncomplicated cases no investigation is required.
Treatment for Diseases of respiratory system
For symptomatic relief-
1. To relieve nasal congestion: Local nasal drops- Nasivion pediatric nasal drops Put 1-2 drops in each nostril for 2-3 times in a day. Discontinue the drops within few days, or when running of the nose has stopped.
2. For fever: Syr. Paracetamol 30-40 mg/kg/day in 4 divided dos- es till the fever subsides. 3. Antihistaminic agent: to relieve na- sal congestion: Pseudoephedrine 4 mg/kg/ day in divided doses- should not be used for prolonged period.
4. Antibiotic is used only in complicated cases with secondary bacterial infection. Syr. Ampicillin 50 mg/ kg/day in divided doses for 5 to 7 days or Syr. Amoxicillin 20-40 mg/ kg/day in divided doses for 5-7 days. Syr. Cefixime mg/kg/day in 2 divided does for 5 days.
BACTERIAL INFECTIONS OF UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT AND Diseases of respiratory system
This includes sinusitis,pharyngitis and tonsillitis.The commonest are pharyngitis and tonsillitis. The commonest organism is beta hemolytic streptococ- cus. Otitis media is also discussed in same topic because it is the commonest complication of untreated or partially treated bacterial infection of the upper respiratory tract.
Sinusitis, pharyngitis and tonsillitis may Occur simultaneously or separately. For the sake of convenience, symptoms and signs of each one of them are discussed separately.
Sinusitis Disease in kids
Symptoms of sinusitis
1. Running of nose: With purulent discharge
2. Heaviness of head
3. It may be associated with fever, malaise or associated pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
Signs
1. Congestion of nasal mucosa
2. Tenderness of maxillary sinus, or frontal sinus
3. Associated pharyngeal conges- tion, post nasal drip and enlarged tonsils Investigations Routinely no investigation is required. In chronic cases X-ray of the para nasal sinuses is advised to confirm the diagnosis.
Complications
If untreated it may lead to otitis media or meningitis.
Treatment of sinus(Diseases of Respiratory System)
1. Local Nasal drops- Shrinkage of nasal mucosa will help in drainage of the sinuses. Nasivion Pediatric nasal drops 2-3 times/day.
2. Antihistaminic drugs like pseudo- ephedrine 4 mg/kg/day in divided doses for 5 to 7 days.
3. Antibiotic: Syr. Ampicillin 50 mg/ kg/day in 4 divided doses for 5 to 7 days OR Syr. Amoxycillin- 20-40 mg/kg/day in divided doses for 5 to 7 days OR Syr. Erythrocin 30-50 mg/kg/day in divided doses for 5 to 7 days OR Syr. Azithromycin 10 mg/kg/day in single dose for 5 to 7 days. Syr. Cefixime 8 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses for 5 to 7 days.
If the child doesn’t settle with the above treatment ENT surgeon’s opinion should be taken for further treatment like antral puncture.
THANK YOU FOR READING
TEAM-DAILYAYURVEDIC